“Role of Government Myth”
In his new book, Stewart Brand states (p. 84):…Energy policy is a matter of such scale, scope, speed, and patient follow-through that only a government can embrace it all. You can’t get decent grid power without decent government power.In reply, Amory Lovins asserts (p. 19, pdf):
…nuclear power requires governments to mandate that it be built at public expense and without effective public participation—excluding by fiat, or crowding out by political allocation of huge capital sums, the competitors that otherwise flourish in a free market and a free society.Lovins’ response contains a contradictory claim. Lovins accuses nuclear of not being able to survive in a “free market and a free society.” Yet, several pages later, Lovins touts how wind and solar are flourishing in China while being built by state-owned power companies according to one of his sources. Further, Lovins’ same source said this about renewables:
A big impetus was the [Chinese] government’s requirement, issued in September 2007, that large power companies generate at least 3 percent of their electricity by the end of 2010 from renewable sources.Doesn’t sound like a free market to me.
Further, nuclear is not “crowding out [other technologies] by political allocation of huge capital sums.” Below is a chart showing the loan guarantee volume available by technology. Nuclear is hardly "crowding out."

As well, Lovins’ section rebutting Brand's role of government logic contains some of the greatest exaggerations yet is also the least sourced. Here is one bogus, undocumented claim from that section (p. 19):
…if all options were unsubsidized and their social costs internalized, the observed market prices suggest that nuclear would lose decisively against practically anything else.Not quite. Below is a graph from the Energy Information Administration that shows the estimated levelized costs for all technologies less subsidies and financing costs. Nuclear is ranked fifth in terms of total levelized costs. Only coal and gas without CO2 controls come in cheaper than nuclear. Renewables are much more expensive. Independent government data illustrated here undermine Lovins' unsupported claims about the costs of renewables and "micropower."
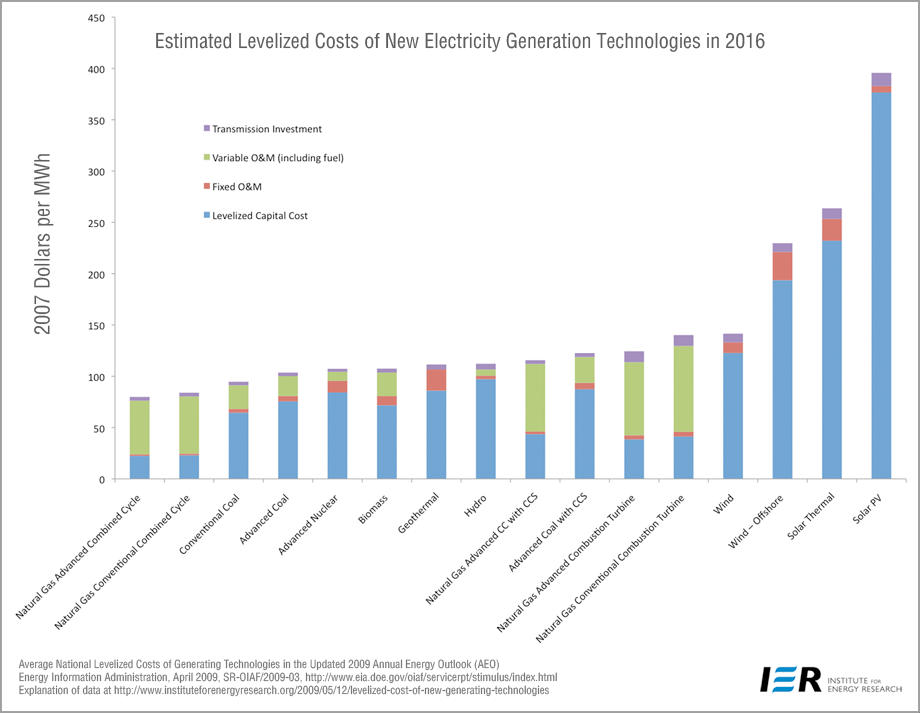
“Sloppy scholarship”
The Lovins study was courteous enough to not only attempt to rebut Brand’s views but also to point out every typo or minor mis-statement in Brand's book. From being a little off about the number of nuclear plants operating worldwide in 2008 to mis-stating by only a few percent nuclear’s worldwide electric share, the Lovins study went hard at Brand’s chapter on nuclear. Let’s pay Lovins’ study the same respect.
The Lovins study incorrectly applies the use of Moore’s law as pointed out in Grist’s comments section.
Referencing one’s previous studies continuously throughout the document as if they’re authoritative pieces of work is lame. It also violates at least one principle of logic.
It’s false to continue to refer to “micropower,” which includes wind and solar, as decentralized technologies when page 26 of this NERC report (pdf) and page 35 of this WADE report (pdf) say wind and solar are mainly central technologies.
Lovins criticizes blogger STK in the Grist comments section saying that STK needs to give more “solid proof” than referencing conversations in an argument when in fact Lovins references conversations at several points in his own paper (p. 5 with Jim Harding, p. 6 with Michael Eckhart, and p. 30 with China’s “top officials”).
A chart on page 27 of Lovins’ paper that compares the electric generation of nuclear to its competitors should no longer be used after it was thoroughly debunked more than a year ago.
And research from Stanford Professor Jacobson shouldn’t have been referenced in the first place because it doesn’t even stand up to scrutiny.
Conclusion
After reading Amory Lovins’ latest paper written only to argue with Stewart Brand, it is clear that the paper tries too hard to make an argument against nuclear. While facts need to be backed up by credible sources, more sources doesn’t necessarily mean better.
Readers who have followed RMI’s papers over the years know that sometimes half of a page could be riddled with sources and needless commentary. Lovins’ papers are polluted with so many stats and sources that it makes the paper’s arguments incoherent, confusing, hard to follow and even contradictory at times.
For the number of sources in Lovins’ latest paper, one would think that everything would be accurate and spot on. Yet, as demonstrated here and earlier, this is not the case. In almost every instance that we have looked into Lovins’ sources, we have found that there is another side to the story his study fails to mention. Nuclear isn’t perfect but neither are “nuclear’s competitors,” despite what a Lovins study portrays.
As Brand points out in his book, more and more environmentalists are coming over to the pro-nuclear side. We’re sure this has an effect on the recalcitrant antis because if Lovins’ paper is a symptom, those stuck in the past will become ever more desperate, vocal and isolated. Brand describes the phenomenon (p. 90):
Older environmentalists talk about nuclear power exclusively in terms of what they see as the four great problems that condemn the technology – safety, cost, waste storage, and proliferation. Those four have no form of positive, only degrees of badness, and they are treated as absolutes. If a reactor accident is possible, then nuclear power is impossible; if the capital costs are high, then nuclear power is impossible, and so on. Absolutes are potent. Once something is seen as a capitalized Absolute Evil, it functions as a premise; everything has to exist in relation to your opposition to it.To me, this speaks exactly to Lovins’ thinking. Brand goes on further to explain what changed his mind about nuclear.
By contrast, the four considerations I began with – baseload, footprint, portfolio, and government-scale – are logics rather than problems. They are relative rather than absolute, which means they invite thinking in terms of trade-offs and risk balancing. And they are open to the positive, treating nuclear as one potential tool to help head off climate change and end poverty worldwide.Well said, hope you’ve enjoyed this series. Props to Rod Adams, Steve Kirsch, Charles Barton, Brian Wang, Sovietologist, Gwyneth Cravens, Stewart Brand and all the other pro-nuke commenters who contributed to the debate to blast this junk study! Also thanks to Jim Slider and RSM here at NEI who reviewed my posts with a critical eye to make sure they remained in check!
Holding all eight logics and problems in mind simultaneously nets out, for me, to a strong argument for expanding nuclear power. From that perspective, I see the four problems of safety, cost, waste handling, and weapons potential differently than I used to. I’ve learned to disbelieve much of what I’ve been told by my fellow environmentalists, and I now think of the four problems the way an engineer does, as design problems. Define them, frame them in a way that is solvable, solve the damn things, and once you’ve got a solution, act on it.
0 comments:
Post a Comment